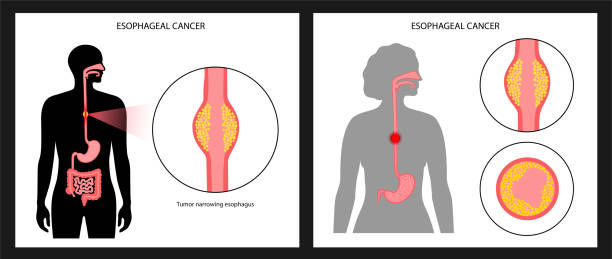
Esophageal cancer is a serious disease. It affects the esophagus, the long tube that connects the throat to the stomach. This cancer starts in the cells lining the esophagus. It can spread quickly if not caught early. Understanding esophageal cancer and its risk factors is crucial for prevention and early detection.
What is Esophageal Cancer?
Esophageal cancer occurs when cells in the esophagus grow uncontrollably. These cells form a tumor. There are two main types of esophageal cancer:
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This type starts in the flat cells lining the esophagus. It usually occurs in the upper and middle parts of the esophagus.
- Adenocarcinoma: This type begins in glandular cells. It often starts in the lower part of the esophagus near the stomach.
Both types can be dangerous and need medical attention.
Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer often does not show symptoms in the early stages. As it progresses, symptoms may include:
- Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia): This is the most common symptom. It may start with difficulty swallowing solid foods and progress to liquids.
- Chest Pain: This can feel like pressure or burning.
- Weight Loss: Unintended weight loss is a common sign.
- Hoarseness: Changes in the voice can occur.
- Coughing: Persistent coughing can be a symptom.
- Indigestion or Heartburn: These can be persistent and severe.
If you experience these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor.
Risk Factors for Esophageal Cancer
Certain factors increase the risk of developing esophageal cancer. Understanding these can help in prevention.
- Age: The risk increases with age. Most people diagnosed are over 55 years old.
- Gender: Men are more likely to develop esophageal cancer than women.
- Smoking: Tobacco use significantly increases the risk. Both smoking and chewing tobacco are harmful.
- Alcohol Consumption: Heavy drinking over a long period increases the risk.
- Obesity: Being overweight can lead to esophageal cancer, especially adenocarcinoma.
- Diet: A diet low in fruits and vegetables can increase the risk. Consuming very hot liquids and processed meats can also be harmful.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Chronic reflux can damage the lining of the esophagus. This can lead to a condition called Barrett’s esophagus, which increases the risk of adenocarcinoma.
- Achalasia: This is a condition where the lower esophagus does not relax properly. It can increase the risk.
- Exposure to Certain Chemicals: Some chemicals, such as lye, can increase the risk if ingested.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): Some studies suggest a link between HPV and esophageal cancer.
Prevention of Esophageal Cancer
While not all cases can be prevented, certain lifestyle changes can reduce the risk.
- Quit Smoking: Stopping smoking can greatly reduce the risk.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Drinking in moderation or not at all can help.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Regular exercise and a balanced diet can prevent obesity.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: Include plenty of fruits and vegetables. Avoid very hot drinks and processed meats.
- Manage GERD: Treating acid reflux can prevent damage to the esophagus.
- Regular Check-ups: If you have risk factors, regular screenings can help catch the disease early.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing esophageal cancer often involves several tests:
- Endoscopy: A camera on a flexible tube is used to view the esophagus.
- Biopsy: A small tissue sample is taken during an endoscopy to check for cancer cells.
- Imaging Tests: CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans help to see if the cancer has spread.
Treatment depends on the cancer stage and type. Options include:
- Surgery: Removing part or all of the esophagus.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Using drugs to target specific cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Living with Esophageal Cancer
Being diagnosed with esophageal cancer can be challenging. Support from family, friends, and healthcare providers is crucial. Joining support groups can also help. It’s important to follow the treatment plan and attend all follow-up appointments.
Esophageal cancer is a serious condition, but understanding it can help with prevention and early detection. Knowing the risk factors and symptoms can save lives. Making healthy lifestyle choices can reduce the risk. Regular check-ups and being aware of any changes in your body are vital. If you have concerns, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes and quality of life.